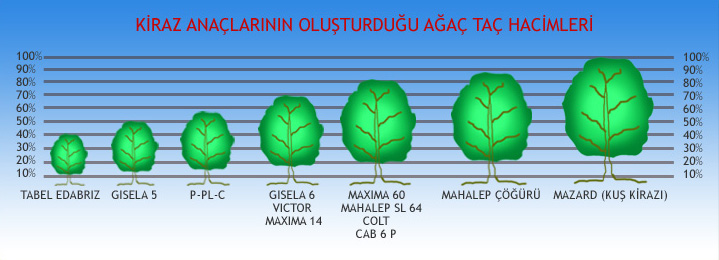
MAHALEP SL 64
- It is included among the clone trees under Mahalep type.
- It is a moderately growing rootstock developing 75-80 percent of generative mahalep.
- They aren't recommended for heavy, clayed soils with high level of underground water.
- Their root system is well developed therefore doesn't need a support system.
- 5m gaps on a line and 3.5-4m gaps between the lines are suitable for the gardens on this rootstock.
- If lime is a problem in the soils, this rootstock might be used for cherry.

GISEL A ROOTSTOCKS
- These rootstocks were developed by crossbreeding the P. Avium P. Canensis species in the Gissen Research Institute in Germany.
- Gisel A 5, Gisel A 6, Gisel A 7, and Gisel A 12 are the most widely used Gisel A rootstocks and dwarf Gisel A rootstock started to be used in recent years.
- Gisel A rootstocks should be used in deep soils with PH below 8, active lime rate lower than 10% and irrigation possibilities.
- Gisel A rootstocks don't enjoy heavy textured soils with high level of underground waters.
- Gisel A rootstocks shouldn't be preferred in very hot regions.
- The most dwarf one is the Gisel A 3 and forms trees sized 35-45% of the rootstock created by Mazzart rootstock (wild cherry), while Gisel A 5 forms 50-55%, Gisel A 6 forms 70-80%, and Gisel A 12 forms 90-95%.
- Gisel A rootstocks have 2-3 years early yielding compared to generative Mazzart rootstock.
- Gisel A 5 and Gisel A rootstocks have tolerance for Prune Dwarf virus and Clorotic Necrotic Ring Spot virus.
- In a place where cherry tree was removed, some problems occur when again cherry trees are on Gisel A 5 rootstock are planted.
- Since too much fruit it gives on Gisel A rootstock, fruits remain smaller. Therefore, gardens should be planted with stocks of especially Sweet Heart, Lapins and Chelan etc. species grafted onto the Gisel A rootstocks.
- Gisel A 5 rootstock can be planted in 4x2.5 gaps and Gisel A6 rootstock can be planted in 4.5x3.5.

MAX MA DELBARD ROOTSTOCK
- It was found as a coincidence generative rootstock in Oregon USA.
- The most important one among the Max Ma rootstocks, hybrid of Mazard and Mahalep, is the Max Ma 14 rootstock and there are Max Ma 60 and Max Ma 90 rootstocks also.
- MaxMa14 is a semi-dwarf rootstock and has the characteristic of Mazard and Mahalep rootstocks.
- It forms tree crown as 70-75% of wild cherry (mazard) rootstock.
- It yields early. It positively affects the fruit size and quality.
- It may form lower shoots even in a few numbers.
- MaxMa rootstocks resist to Pseudomonas disease.
- They are resistant to colds.
- They aren't recommended for heavy textured soils with poor drainage.
- They are mainly used in Spain and French.

CAB ROOTSTOCK
- They were regenerated in Bologna University in Italy.
- CAB 4D, CAB 11E and CAB 6P are the most important rootstocks included in this series.
- They are included in Prunus Cerasus (sour cherry) and may be recommended as rootstock for sour cherries.
- They have been tried for 30 years in Italy and widely used.
- They can be used in heavy textured soils.
- It forms 50-60% of the tree volume formed by wild cherry, grows same as Ma x Ma 14 rootstock.
- It yields 2 years earlier compared to generative rootstock.
- It produces lower shoots even if a few, reproduction by cutting is hard.
- It is resistant to colds.

P-HL ROOTSTOCKS
- These rootstocks were evolved by crossbreeding the Prunus Cerasus and Prunus Avium species in Czechoslovakia and most important rootstock are P-HL-A, P-HL-B and P-HL- C.
- They have a shallow root system.
- Resistant to cold climate conditions.
- They can reproduced with tissue culture.
- Among the rootstocks under this group, P-HL-C rootstock is the most dwarf one and forms 40-50% of the wild cherry standard generative rootstock.
- They need a support system in windy areas.
- They are partly resistant to heavy textured soils.

WEIROOT ROOTSTOCK
- Cherry rootstocks developed from Prunus cerasus specie in Germany.
- Most important ones are Weiroot-158 and Weiroot -54.
- It allows the specie on it yield earlier.
- It forms trees 40-45% of the crown created by wild cherry generative rootstock.

VICTOR ROOTSTOCK
- It was regenerated in Bologna University in Italy.
- It is among the semi-dwarf rootstocks.
- Regenerated from the Prunus Cerasus specie.
- A good rootstock for fruit size and productivity.
- Moderately resistant to lime, underground water and aridity.
- 3-3.5m gaps on the line and 4-4.5m gaps between the lines are good for this rootstock.

Characteristics of Some Cherry and Sour Cherry Clone Rootstocks
|
ROOTSTOCK
|
TREE GROWING ABILITY |
RESISTANCE TO LIME |
RESISTANCE TO UNDERGROUND WATER |
RESISTANCE TO ARIDITY |
PLANT SPACING GAPS |
|
Victor
|
4,5m x 3,5 m | ||||
|
Cab 6 p
|
5 m x 4 m | ||||
|
Ma x Ma 14
|
5 m x 4 m | ||||
|
Ma x Ma 60
|
5 m x 4 m | ||||
|
Gisela 5
|
4,5 m x 2,5 m | ||||
|
Gisela 6
|
4,5 m x 3,5 m | ||||
|
SL 64
|
5 m x 4 m | ||||
|
Colt
|
5 m x 4 m | ||||
|
P-HL-C
|
4,5 m x 2 m | ||||
|
WILD CHERRY (MAZZARD) |
5 m x 5 m | ||||
|
MAHALEP
|
5 m x 5 m |